How to organize your keyword lists
Keyword research is a fundamental tactic that can completely transform the overall marketing strategies of those who take it seriously. Ann Smarty explains
Keyword research is a fundamental tactic that can completely transform the overall marketing strategies of those who take it seriously. Ann Smarty explains
Keyword research is a fundamental tactic that I have seen completely transform the overall marketing strategies of those who take it seriously.
In fact, just about any marketing area begins with keyword research, be it competitive analysis, traffic growth, content planning, or PPC strategy. It has always been the foundation of online marketing and it still is – even though it’s rapidly evolving.
I have seen clients go from barely functioning marketing plans to full-scale content marketing projects that up their rankings and conversions. Keywords are serious weapons.
Keyword lists are messy. They contain every little variation of each particular query because they include whatever enough people spontaneously type into the search box.
We search in a more disorganized way than we speak. For example, we could search ‘research keywords’, ‘how to research keywords’, ‘research keywords how to’, ‘keyword research tips’, or even ‘keyword research how to tips’ – and all of that will basically mean the same thing (i.e. we want to know how to research keywords).
Keyword research tools like SEMrush and Ahrefs will provide you with hundreds of thousands of those keyword strings (as well as marketing inspiration).
But, how do you make sense of all those lists that leave us with a huge pile of dumped keywords organized with no rhyme or reason? How do you turn them into plans and actions?
This is precisely why you should be taking the time to organize your keywords. It might not be a very fun process, but it is a very important one.
Here are some tips.
One popular way to organize your keywords is by usefulness of the keyword. How you define that is up to you, but many marketers categorize it by price per click balanced with the projected click rate. They also look at how likely it is that the keyword would help them rank on the first page or (more recently) get a featured snippet:
Featured tool: I like using Ahrefs “clicks” data to determine most useful phrases, i.e. phrases that are able to send a lot of traffic, and those where my site ranks pretty well already:
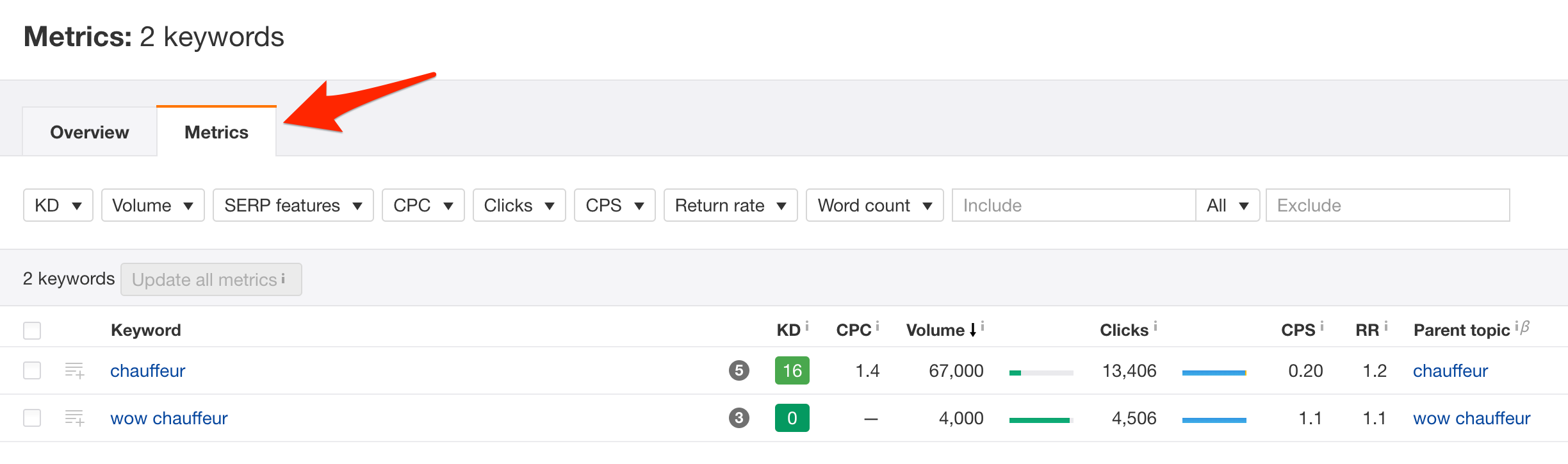
[No other keyword research tool beats this insight.]
The abundance of keyword strings in your lists often mean pretty much the same thing. They are always in your way preventing you from focusing on other important aspects of keyword research, so getting rid of those (or rather grouping them) is the first thing to do.
This is where keyword clustering comes in handy. I have already explained the tactic in detail here.
Featured tool: Serpstat looks at Google SERPs for each phrase and determines related queries by overlapping URLs. This is pretty much the only tool that can do that, to the best of my knowledge:
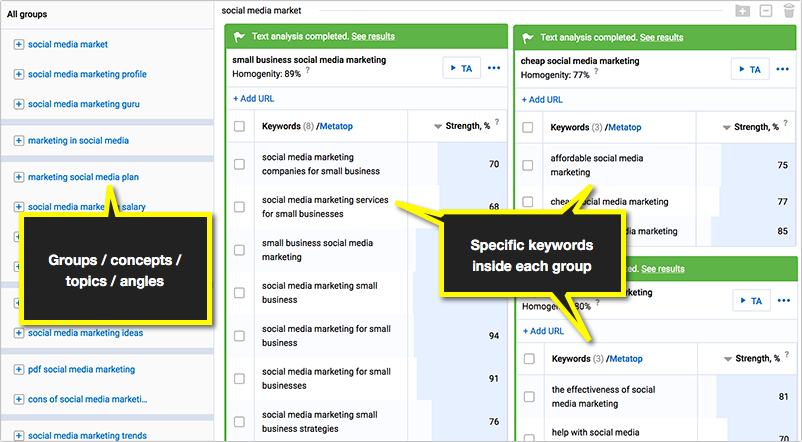
Another way to organize keywords is by intent, which is usually more straightforward. Set some goals about what you want to accomplish – not just with keyword research but your whole brand. Use that to inform your keyword strategy and separate each goal by intent so you have a list of keywords for each.
Say that you want to target the market for affordable time management programs. You will want to increase brand visibility, get a featured snippet in a popular query and bring more attention to your social media. Make keyword lists for those three goals.
Usually search intent puts keywords into four groups:
Featured tool: searching Google itself will give you some idea on what Google has found the intent to be. For example, if you see shopping results, you can be fairly sure Google has come to the conclusion that most of these searchers wanted to buy things.
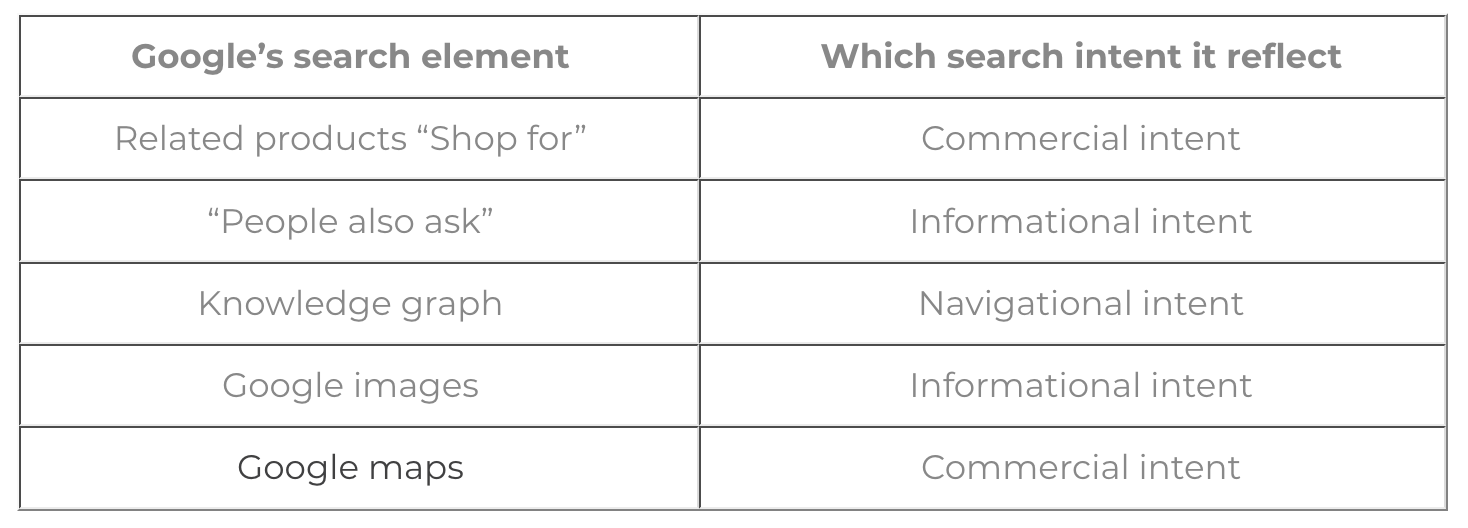
[Chart source: Digitaleagles.]
These should be a separate tab in your spreadsheet. Every company needs to make it easier for people to find you. Do this based on your brand name, [competitor alternatives], etc., which is an easy way to make sure your bases are covered and a simple way to organize your research.
Another way to do this is to target phrases that are negative and then prove them wrong with content. An example would be a phrase like, “Is [product name] a scam?” When users search it, they will find that no, you are not a scam and are not listed on any scam sites. This reassures them, even though the original search was negative.
Don’t forget to research all kinds of queries your (or your competitors’) brand includes:
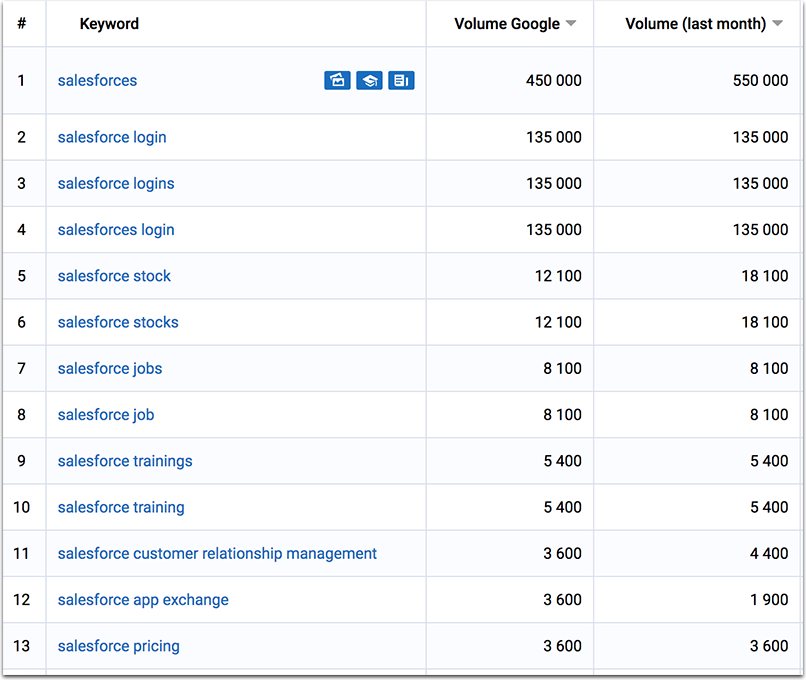

[You may also want to label these queries by sentiment to give your content team more clues on how to address each one.]
I always do these in their own list. A modifying keyword is one that uses an adjective to describe what is being searched for. For instance, they may search for ‘cheap project management platform’ or ‘free ways to manage teams’.
Words like free, cheap, top, best, etc., are fantastic modifiers and are easy to organize in their own section. Once you have had some trial and error you will know which work best.
Organizing by modifiers helps you evaluate your niche trend to match your content and conversion funnel strategy. Do your potential customers tend to search for cheap or exclusive types? Are they looking for DIY or pre-built solutions? Organizing by modifiers gives all those important answers.
I wrote about this type of keyword organizing in an older article at Moz:
Finally, make sure you are using as much information as possible. Add volume/clicks, difficulty and anything else you can think to use. You may also consider adding labels for which type of action each keyword requires:
As well as page type it’s good for, e.g.:
There may be more labels if you are optimizing a local business website. Michael Gray described some in his article here.
That information should also include how it is working over time. I have made graphs with Excel using the data and gotten a much clearer picture of what is and isn’t bringing in the results I want. You can tweak from there.
Do you have a tip for organizing keywords? Let us know in the comments.